This verb is made more complex by the fact that in attic greek that is the dialect of most of the major classical authors the present tense apart from the indicative mood imperfect tense and future are usually replaced by parts of the irregular verb εἶμι eîmi i will go.
Imperfect imperative attic greek.
We were eating in the following sentence would be expressed using the imperfect in hellenistic greek.
While it is among the most commonly used tenses of finite verbs there is no infinitive form of the imperfect.
Analytical lexicon for the koine bible.
Verbs are the words of action.
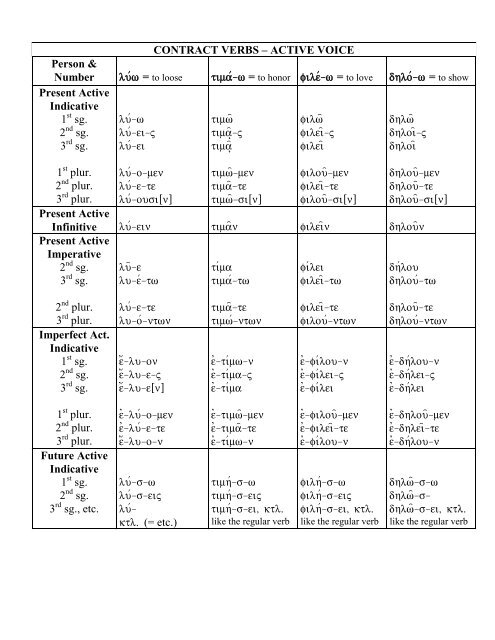
The present active indicative verbs are the foundation for all greek verbs.
There are three steps to forming this tense.
Grammatical discussion imperfect active indicative.
Hellenistic koine present imperative 2nd person singular.
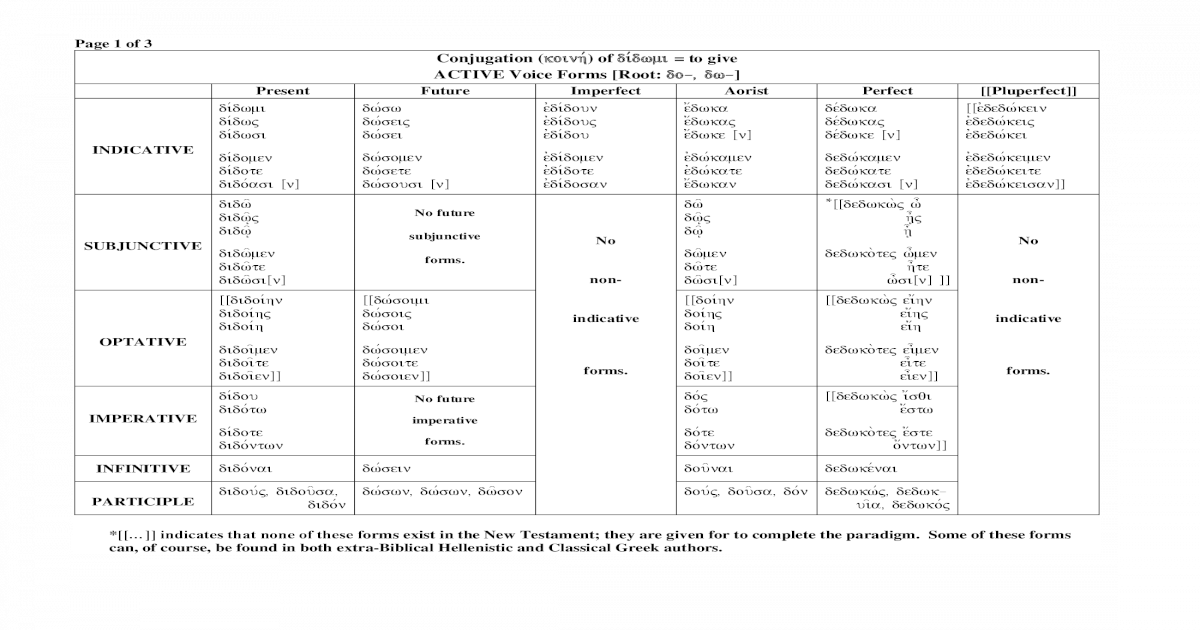
Tense voice mood person and number.
Imperative mood in greek posted by ourania on may 18 2016 in grammar.
In the greek conception the imperfect tense is essentially the present tense shifted back into the past.
Aor act ind 3rd sing.
This mood is to be found in the ενεστώτας simple present αόριστος simple past and seldom in the παρακείμενος present perfect.
In oral speech the imperative is used frequently in order to express a command a request or prohibition.
The first secondary tense that we are learning is the imperfect.
The indicative of εἶμι eîmi is generally used with future significance in the classical period i will go but the other parts such as the infinitive ἰέναι iénai to go are not future.
This post is an introduction to the imperative mood with examples on its use.
As we previously learned the perfect tense is a primary tense.
Anneloesf under a cc license on flickr.
Since the perfect and pluperfect tenses reflect the same aspect in greek they both are formed from the perfect stem s 1852b.
Aktionsart aspect and time.
The pluperfect however is a secondary tense and so must be inflected with an augment and secondary endings.
So let s take it one step at a time.
To burst apart crack open forms.
The imperfect indicative represents an action as going on in past time as ἔλῡον i was loosing or i loosed.
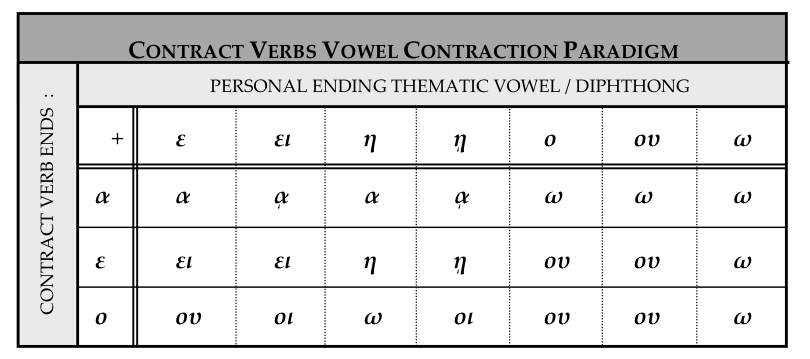
This table gives attic inflectional endings.
The imperative is used in the 2nd and the 3rd person.
For conjugation in dialects other than attic see appendix ancient greek dialectal conjugation.
Scholars propose three uses of tenses in greek.
Some argue that tenses.
The greek verb has following grammatical categories.